
- #L298n motor driver four motors how to#
- #L298n motor driver four motors full#
- #L298n motor driver four motors Pc#
- #L298n motor driver four motors series#
If both the inputs are either HIGH or LOW the Motor B will stop.ĮNB pins are used to control speed of Motor B. When one of them is HIGH and other is LOW, the Motor B will spin. IN3 & IN4 pins are used to control spinning direction of Motor B. If both the inputs are either HIGH or LOW the Motor A will stop. When one of them is HIGH and other is LOW, the Motor A will spin. IN1 & IN2 pins are used to control spinning direction of Motor A. Removing the jumper and connecting this pin to PWM input will let us control the speed of Motor A. Pulling this pin HIGH(Keeping the jumper in place) will make the Motor A spin, pulling it LOW will make the motor stop.
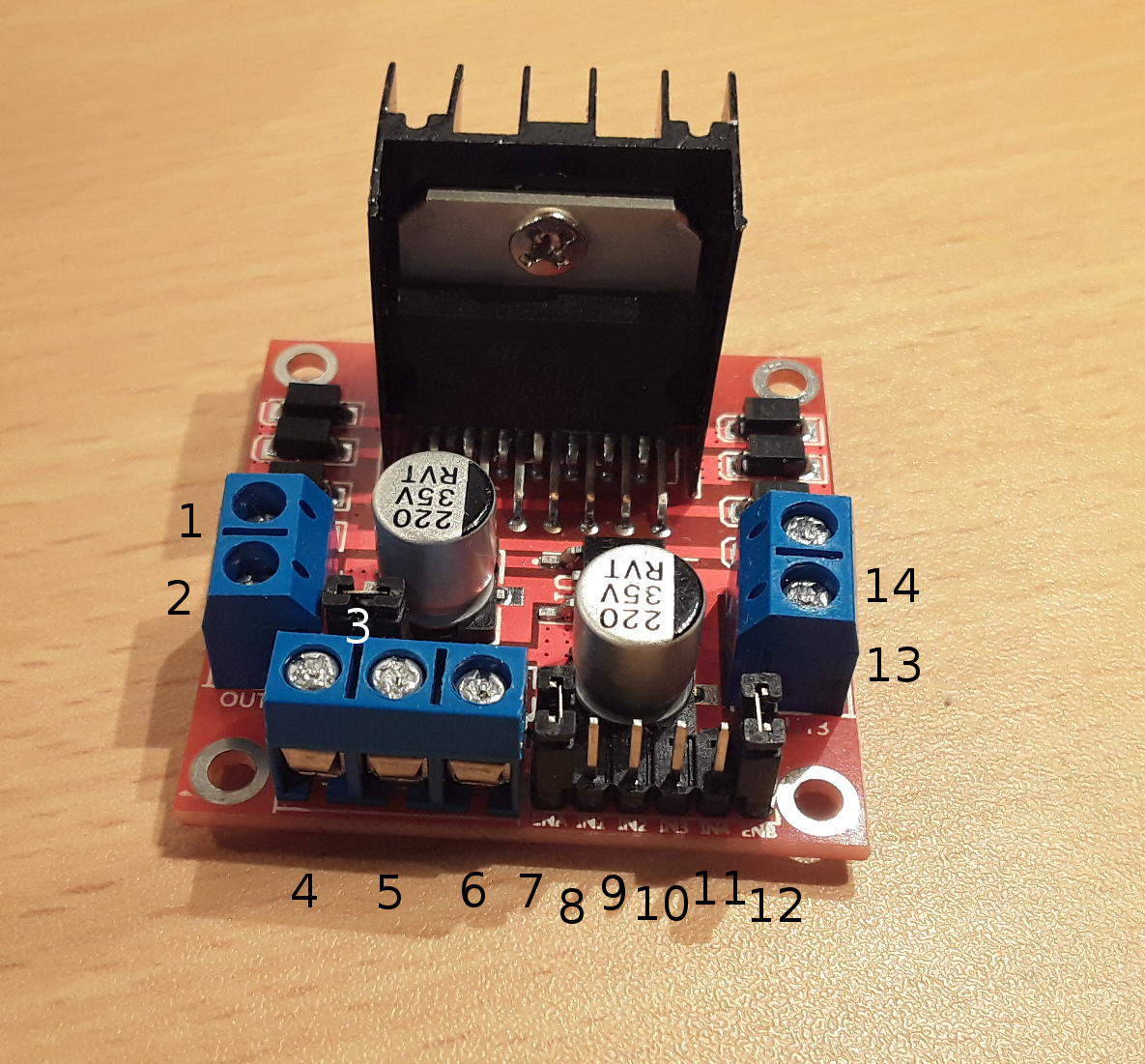
If the 5V-EN jumper is removed, you need to connect it to the 5V pin on Arduino.ĮNA pins are used to control speed of Motor A. If the 5V-EN jumper is in place, this pin acts as an output and can be used to power up your Arduino. Remember, if the 5V-EN jumper is in place, you need to supply 2 extra volts than motor’s actual voltage requirement, in order to get maximum speed out of your motor.ĥV pin supplies power for the switching logic circuitry inside L298N IC. The higher the duty cycle, the greater the average voltage being applied to the dc motor(High Speed) and the lower the duty cycle, the less the average voltage being applied to the dc motor(Low Speed).īelow image illustrates PWM technique with various duty cycles andaverage voltages. The average voltage is proportional to the width of the pulses known as Duty Cycle.
#L298n motor driver four motors series#
PWM is a technique where average value of the input voltage is adjusted by sending a series of ON-OFF pulses. A common technique for doing this is to use PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) The speed of a DC motor can be controlled by varying its input voltage.
#L298n motor driver four motors Pc#

#L298n motor driver four motors how to#
How to Connect Easy Driver Micro-Stepper Controller to Arduino.Considerations for Using Stepper Motors.Connecting the Arduino to a L298N H-Bridge.L298N Motor Controller Theory and Projects.In the proceeding sections we will connect the L298N to a micro-controller to operate a bi-polar stepper motor and explore using pulse-width-modulation (PWM) to control motor speed on a standard DC motor.
#L298n motor driver four motors full#
This completes our introduction to the L298N dual full bridge driver. This is in my opinion the smart way to go to save time, money, and effort. This included power connectors, diodes, LED indicators, and even a 5-volt regulator. Shown above is a pre-assembled board I bought off Ebay for $8 with shipping. ENA and ENB can be connected directly together to enable both channels at once or simply tied to +5 volts and both channels making all four outputs active at all times.Ī 5-volt TTL level input to In1, In2 In3, or In4 will produce a corresponding output of Vm (motor voltage) minus about a volt. ENA will turn on A1 and A2 when with a digital HIGH (5-volts) and off when LOW (0 volts) the corresponding outputs will be floating when off. The current sense pins in general can be tied to ground, but one can insert low value resistor, whose voltage reading is proportional to current.ĮNA, ENB, and In1-In4 are all standard 5-volt TTL logic making connection to most micro-controllers easy. The four power amplifiers and grouped in pairs of two with individual enable pins (ENA, ENB) and individual current sense pins (CSA, CSB) for each pair. Perhaps an updated version will include these internally. I have used more common 1N4001 rectifier diodes and they seem to work fine. One of the annoying features of the unit is the lack of internal parasitic (flywheel) diodes to deal with voltage spikes. Pictured above is the basic L298N circuit used to drive inductive/magnetic loads.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
